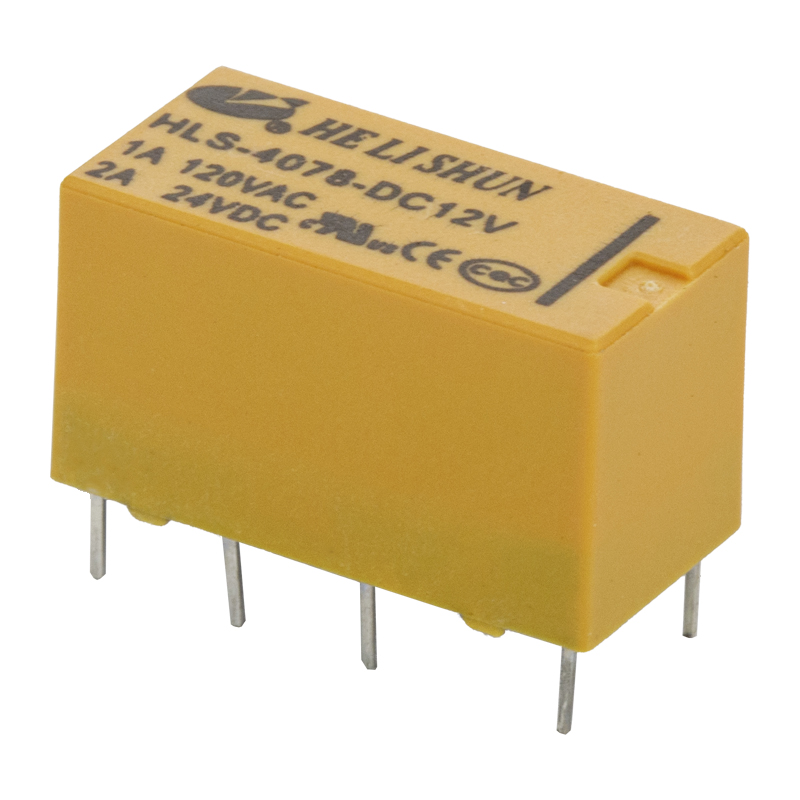
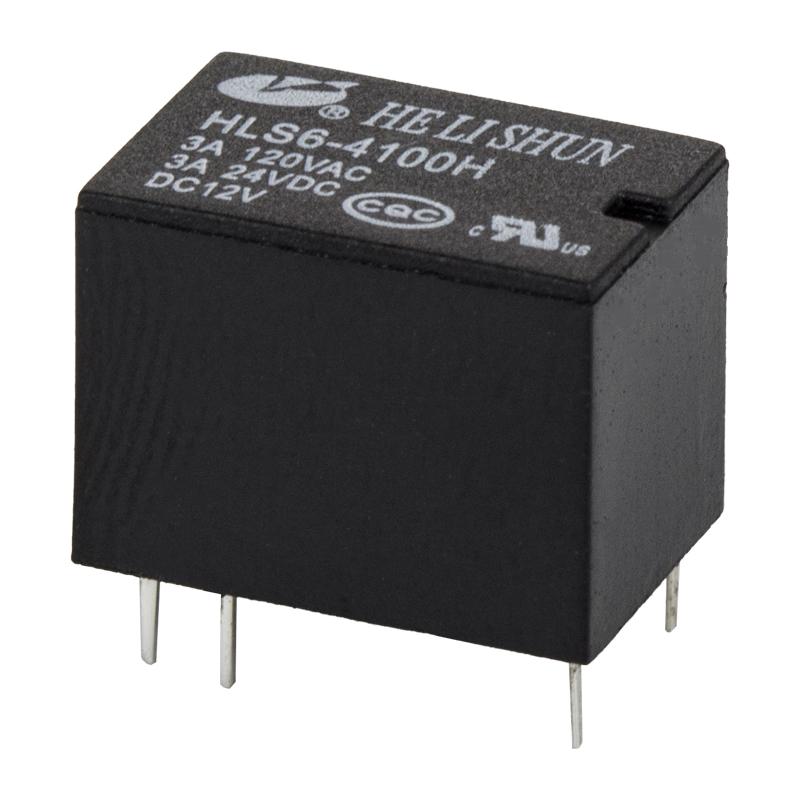
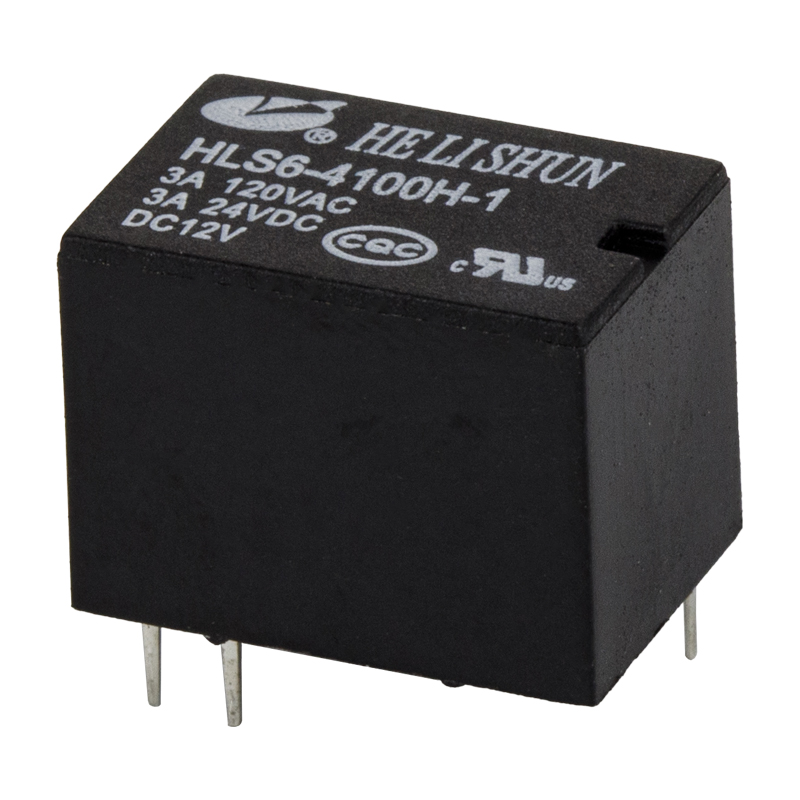
A relay is an electrical device that connects or disconnects a circuit according to changes in electrical quantities (such as voltage, current, etc.) or non-electrical quantities (such as heat, time, pressure, speed, etc.) to achieve automatic control and protection of electric drive devices. The relay is generally composed of three basic parts: the sensing mechanism, the intermediate mechanism and the actuator. The sensing mechanism transmits the sensed electrical quantity to the time mechanism, and compares it with the rated setting value. When the setting value (over or under) is reached, the intermediate mechanism will make the actuator act to turn on or off. Open the controlled circuit.
There are many types of relays, which can be divided into control relays and protection relays according to their uses; according to the nature of input signals, they can be divided into voltage relays, temperature relays, current relays, time relays, speed relays, pressure relays and temperature relays, etc.; according to the working principle can be divided into For electromagnetic relays, inductive relays, thermal relays and electronic relays, etc.; according to the action time can be divided into instantaneous relays and delay relays.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体