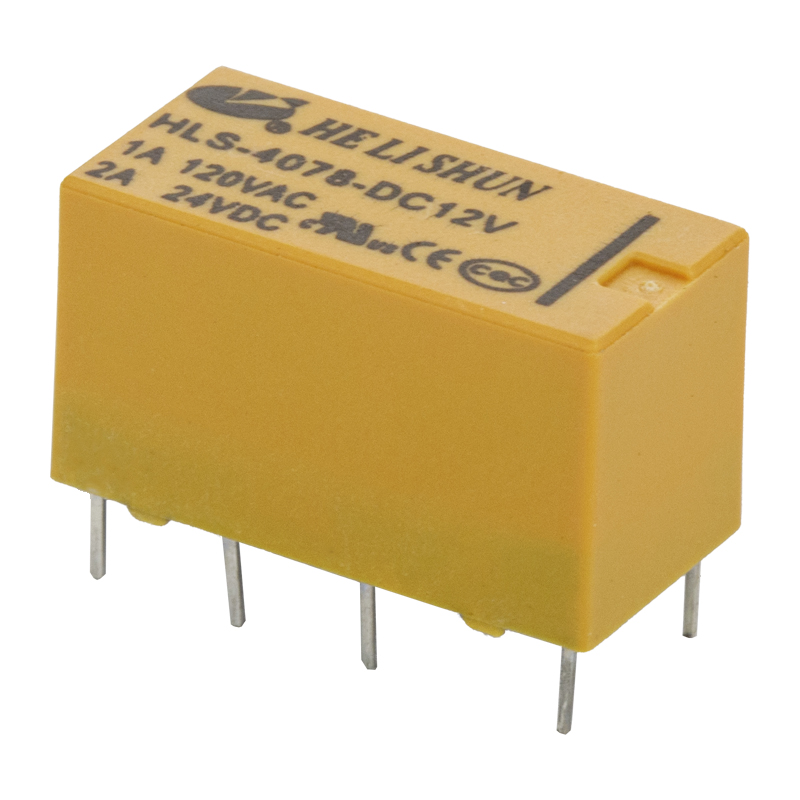
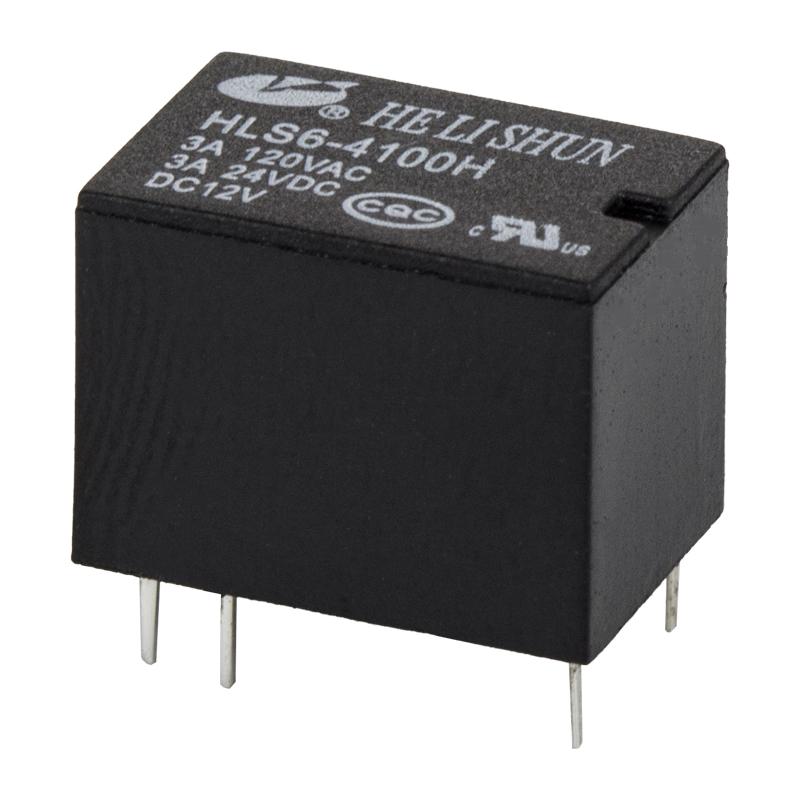
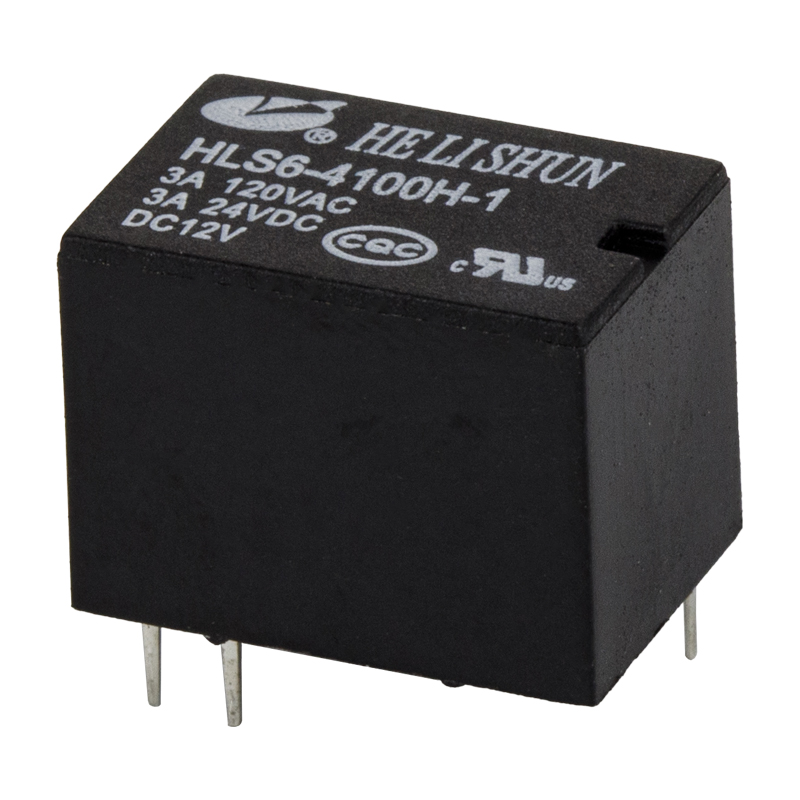
1. The working principle and characteristics of electromagnetic relay
Electromagnetic relays are generally composed of iron cores, coils, armatures, contacts, etc. As long as a certain voltage is applied to both ends of the coil, current will flow in the coil, resulting in an electromagnetic effect, and the armature will overcome the pulling force of the anti-spring and attract to the iron core under the action of electromagnetic attraction, thereby driving the moving contact of the armature. The point and the static contact (normally open contact) are pulled together. When the coil is powered off, the electromagnetic suction also disappears, and the armature will return to the original position under the reaction force of the spring, so that the moving contact and the original static contact (normally closed contact) are attracted. In this way, it is pulled in and released to achieve the purpose of turning on and off the electricity.
The "normally open" and "normally closed" of the relay can be distinguished in this way; if the relay coil is not energized and is in an off state, it is a static contact, which is called a "normally open contact", and a static contact in an on state is called a static contact. It is a "normally closed contact".
2. The working principle and characteristics of sensitive reed relays
Thermal reed relays are new thermal switches that use thermal magnetic materials to detect and control temperature. It consists of a temperature-sensing magnetic ring, a constant magnetic ring, a dry reed switch, a thermally conductive mounting piece, a plastic substrate and other accessories. The thermal reed relay does not use coil excitation, but the magnetic force generated by the constant magnetic ring drives the switch action. Whether the constant magnetic ring can provide magnetic force to the dry reed is determined by the temperature control characteristics of the temperature-sensing magnetic ring.
3. The working principle of solid state relay (SSR)
A solid state relay is a four-terminal device with two terminals as output terminals, and an isolation device is used in the middle to achieve electrical isolation of input/output.
Solid state relays can be divided into AC type and DC type according to the type of load power supply. According to the switch type, it can be divided into normally open type and normally closed type. According to the isolation type, it can be divided into hybrid type, transformer isolation type and photoelectric isolation type. In practical applications, the photoelectric isolation type is the most.
4. The working principle and characteristics of the current relay
A current relay is a relay that makes or breaks a circuit according to the magnitude of the current in the coil. The coil of the current relay is connected in series in the circuit. In order not to affect the working condition of the circuit, the current relay attracts less coils and thicker wires. When the coil current is higher than the set value, the relay is called an overcurrent relay; when the coil current is lower than the set value, it is called an overcurrent relay. It is an undercurrent relay.
When the overcurrent relay is in normal operation, the current passing through the current coil is the rated value, so the generated electromagnetic force is not enough to overcome the reactive elastic force; the normally closed contact remains closed, and when the current passing through the coil exceeds the set value, the electromagnetic attraction force is greater than Reaction spring tension, the iron core attracts the armature, so that the normally closed contact is disconnected and the normally open contact is closed. Commonly used for loss of field protection of DC motors and magnetic chucks.
5. The working principle and characteristics of thermal relay
Thermal relay is a protection circuit that uses the thermal effect of current to switch circuits, and is used as overload protection for motors in the circuit.
The working principle of the thermal relay: when the motor winding causes an overload current due to overload, the heat generated by the heating element is enough to bend the main bimetal, and push the guide plate to move to the right to push the temperature compensation sheet to make the push rod rotate around the axis, and push the contact. The head connecting rod separates the moving contact and the static contact, so that the contactor coil in the motor circuit is de-energized and released, and the power is cut off, which plays a protective role.
The temperature compensation sheet is used to compensate the influence of the ambient temperature on the action accuracy of the thermal relay; it is made of the same type of bimetallic sheet as the main bimetallic sheet.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体