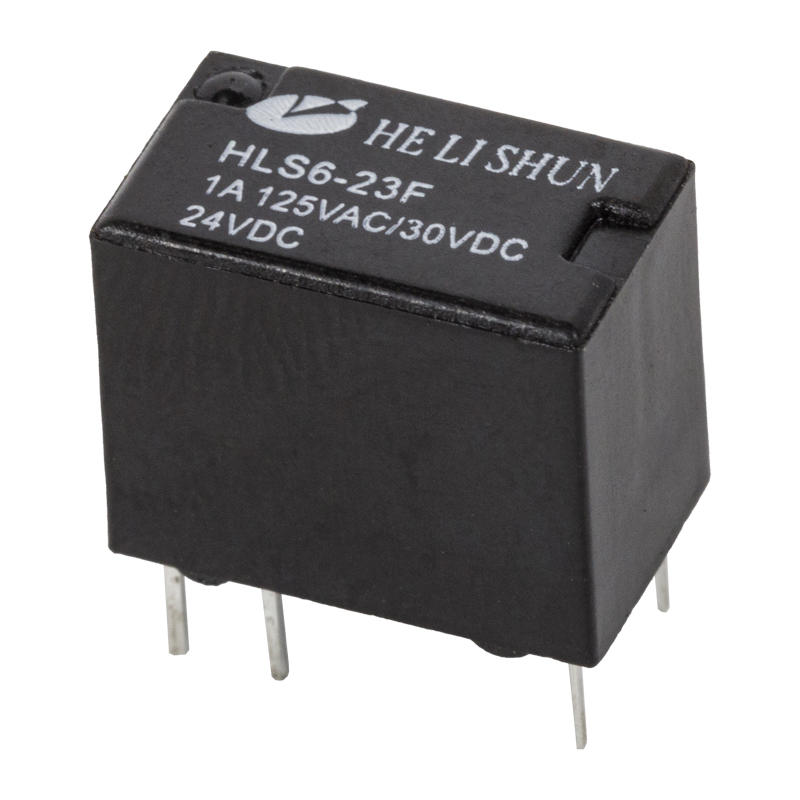
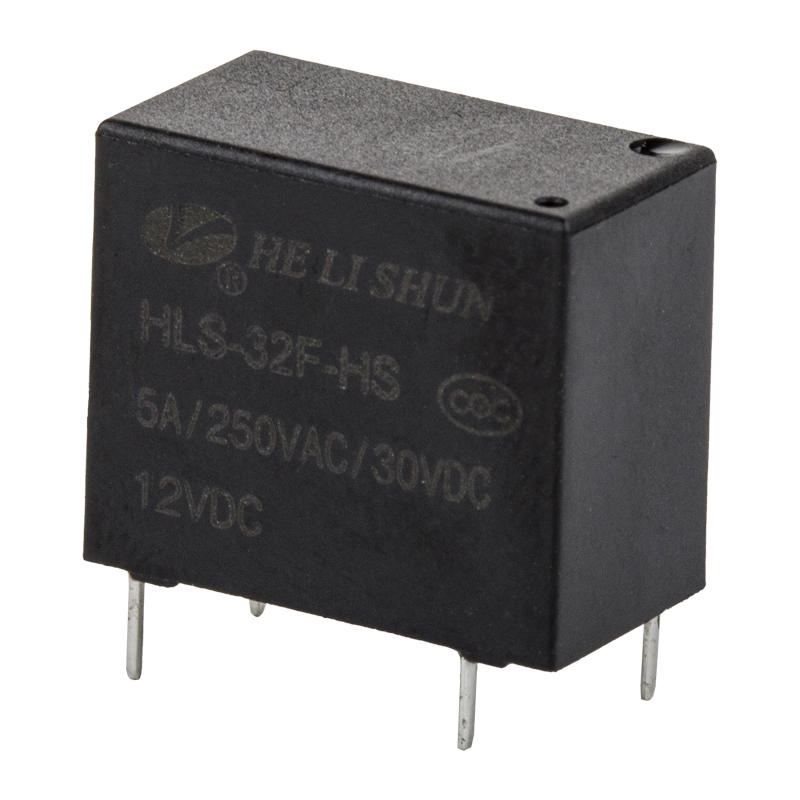
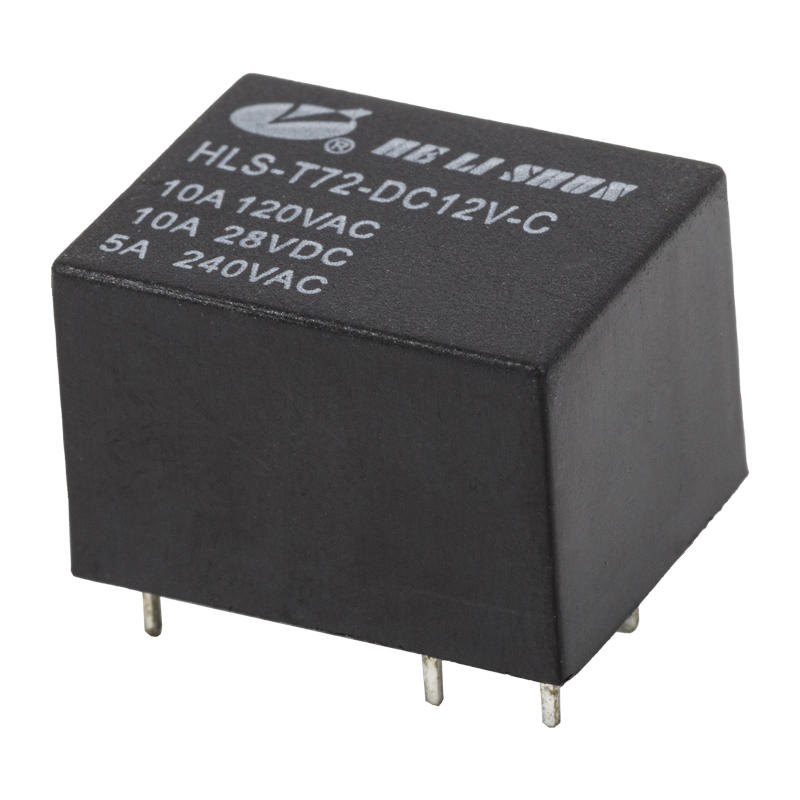
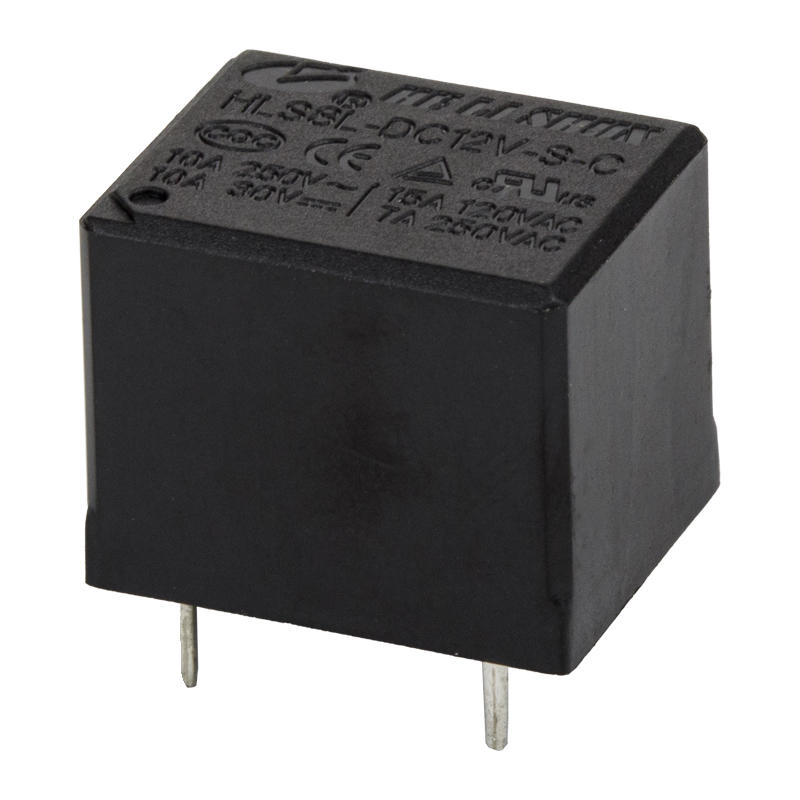
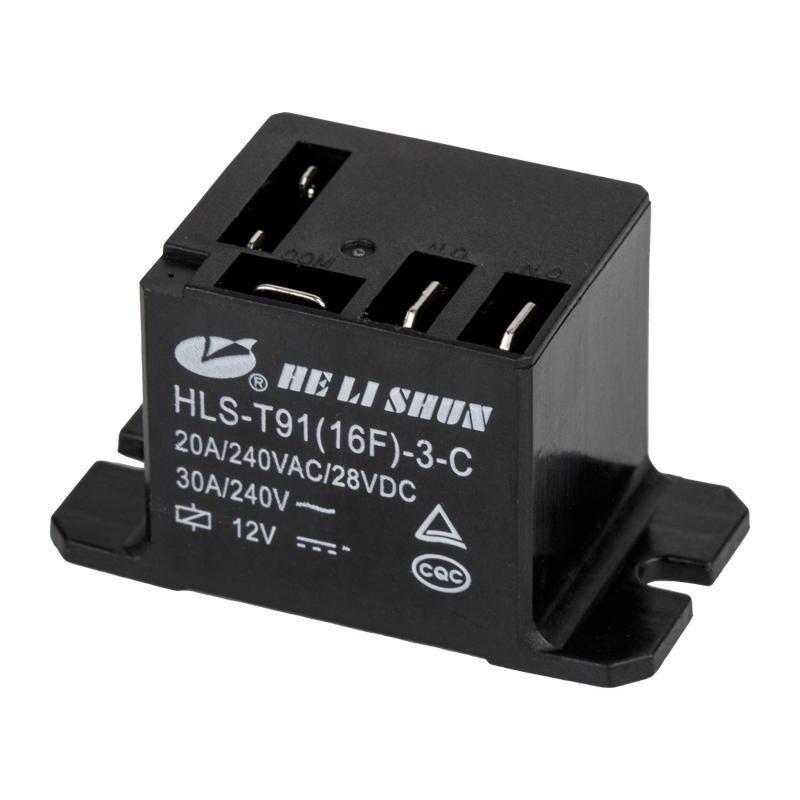
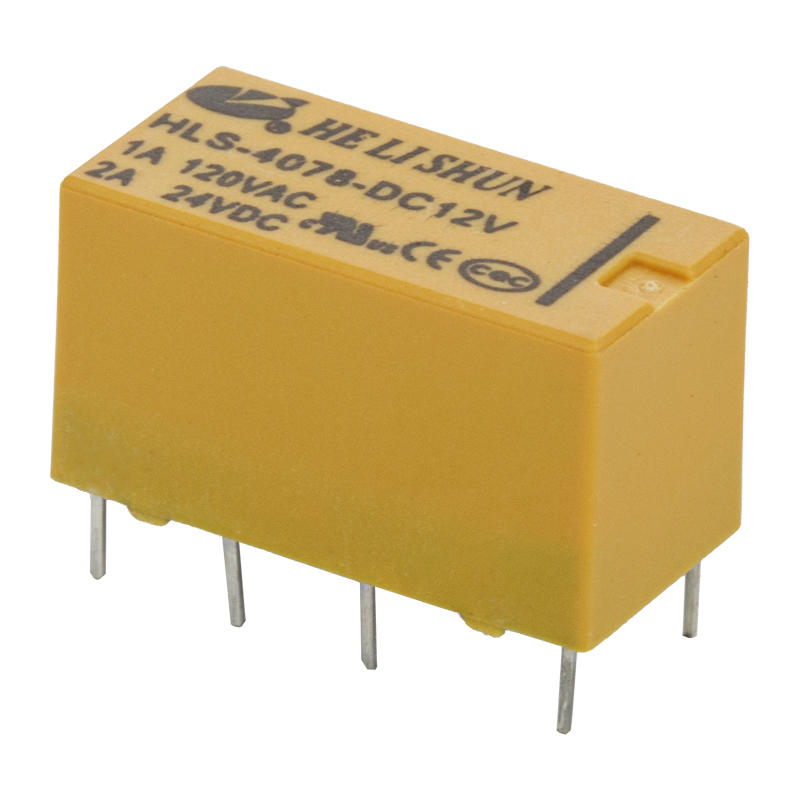
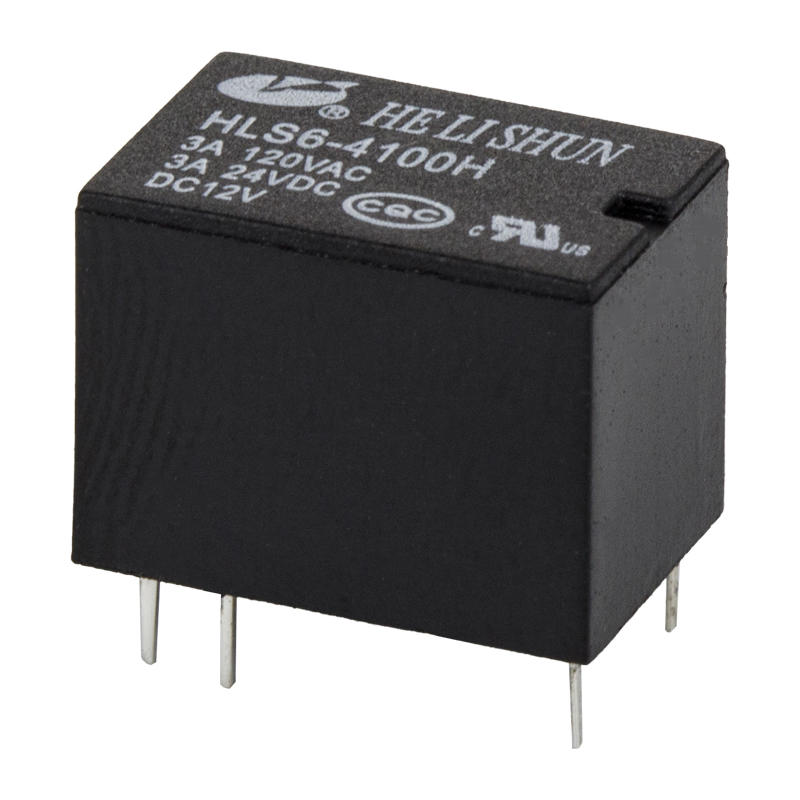
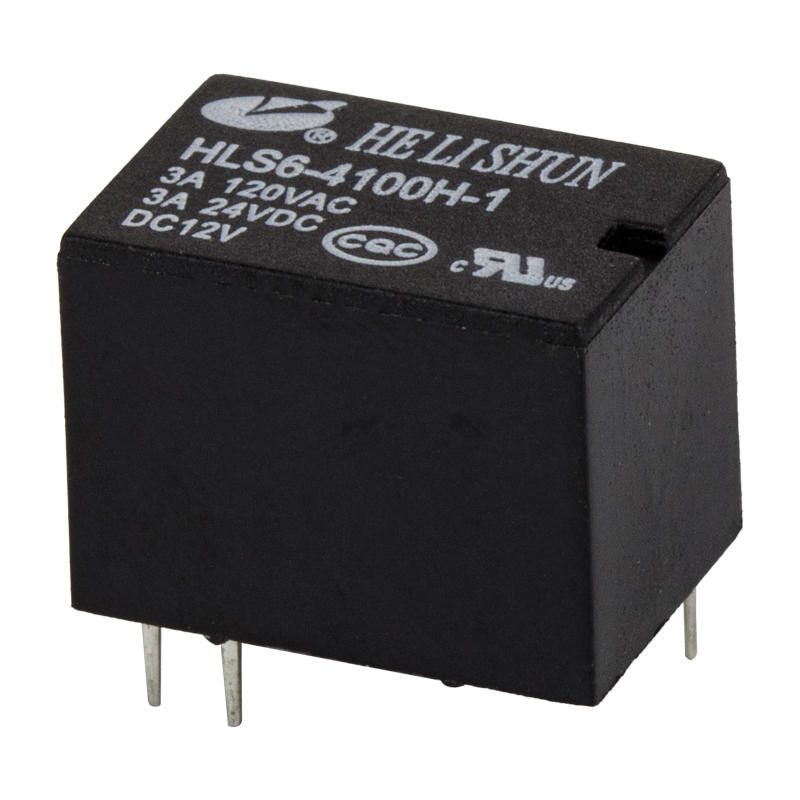
Components of a relay
The automotive relay consists of a magnetic circuit system, a contact system and a recovery mechanism. The magnetic circuit system consists of iron core, yoke, armature, coil and other parts. The contact system consists of static reeds, moving reeds, contact bases and other parts. The recovery mechanism consists of a recovery reed or a tension spring.
installation method
1. Installation direction If the installation direction is consistent with the direction of the shock resistance of the relay, the performance of the relay can be fully exerted. It is recommended to make the impact direction perpendicular to the movement direction of the contact and the armature, which can effectively improve the vibration resistance and impact resistance of the normally closed contact in the non-excited state. When installing, make the contact axis of the relay parallel to the ground, which can avoid contact splashes and carbides falling on the contact surface and improve the contact reliability. Multiple groups of relays should avoid that the small load contacts are located below the large load contacts.
2. Proximity installation When multiple relays are installed in close proximity, it will cause abnormal heat generation. Generally, a spacing of 2mm is recommended. Polarity or latching relays installed in close proximity will affect the operating voltage.
3. When the relay is installed on the casing, it is not possible to remove the casing and install it first. To prevent loosening, damage and deformation, please use a spring washer. The tightening torque should be within the range of 0.5 to 70N·m.
4. The insertion strength of the plug-in relay is recommended to be 40-70N.
5. Products that meet the same load requirements have different dimensions. According to the allowable installation space, products with low height or small installation area can be selected.
6. The installation methods of automotive relays include PCB board type, ISO socket installation type, ISO 280 socket installation type, shell fixing, and card installation. For relays with small size and infrequent replacement, PCB board type is generally used, and for frequently replaced relays, socket installation method is used. For relays whose main circuit current exceeds 20A, the socket quick-connection type is generally used to prevent high current from passing through the circuit board and causing heat damage to the circuit board (except for short-term work relays). For bulky relays, the shell-mounted type can be selected to prevent damage to the mounting feet under shock and vibration conditions.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体