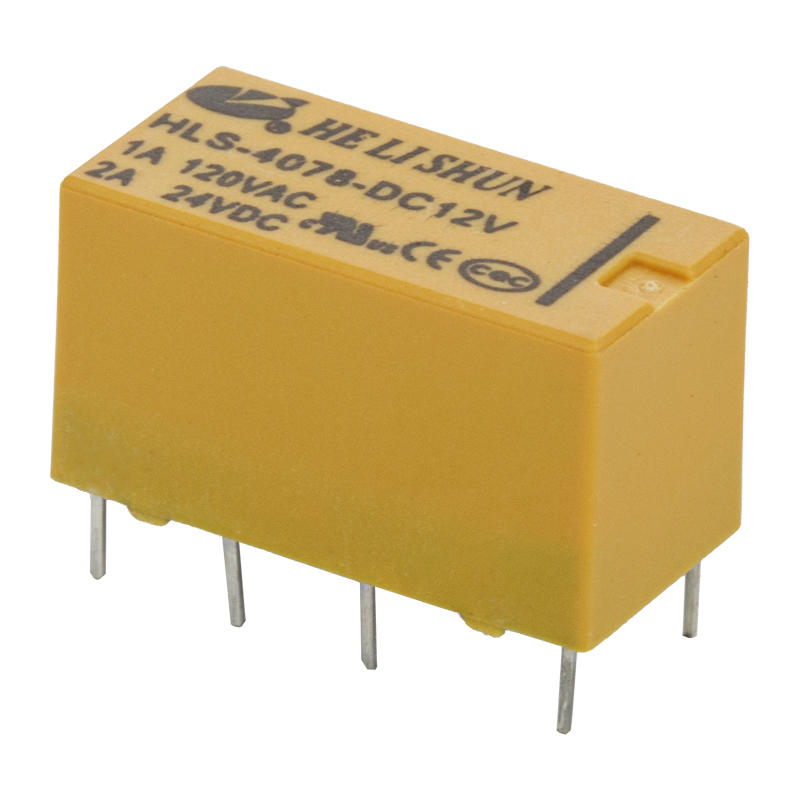
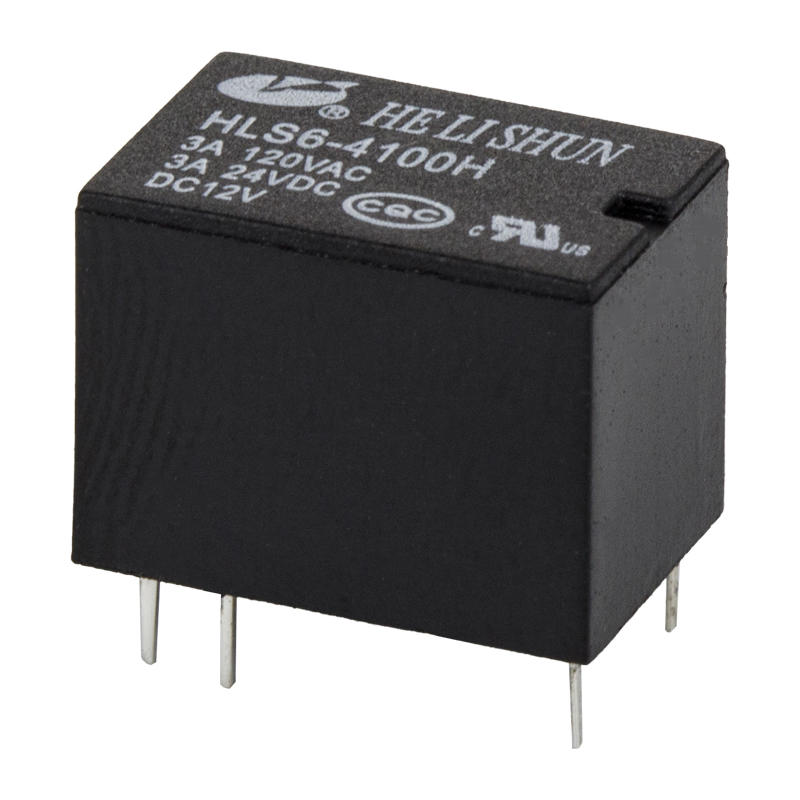
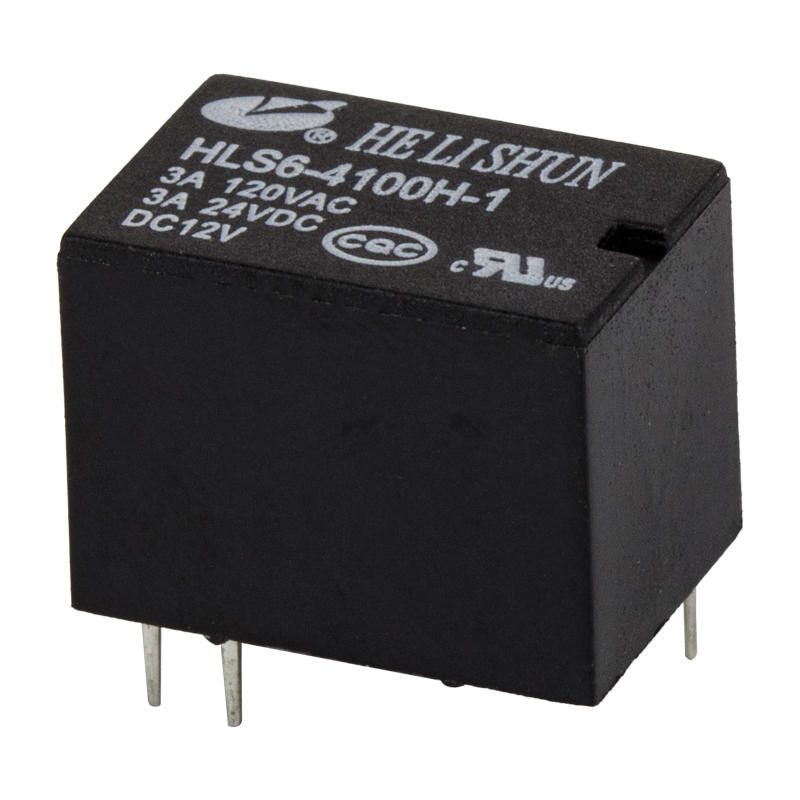
Essentially, an electrical relay is a mechanical switch used in devices such as traffic signal controllers. Its primary function is to switch on or off. It can be powered by DC or AC. It is usually used to control circuits that carry less than 20 amps.
Relays are composed of an iron core that contains a movable, spring-loaded part called the armature. This is attracted to the magnetic field when the relay is energized. The armature also closes electrical contacts when the relay is de-energized.
Relays are made from many different materials. These materials are used to ensure that the contacts operate properly. Some relays use copper contacts, which have a high contact resistance. Other relays use silver nickel contacts, which have a fine grain structure. Silver nickel contacts help reduce the effects of pitting.
Relays use three different contact pinouts. A contact that is normally open is known as Form A contact, while a contact that is normally closed is called Form B contact.
An electrical relay can also have more than one pole. A single pole switch is normally denoted as SP, and a double pole switch is DP. Double pole switches allow two circuits to be switched simultaneously.
Electrical relays can be powered by DC or AC. Relays are often used in televisions and temperature controllers. They are also used in automatic stabilizers. They can be used to switch picture tube televisions, which require a high AC voltage.
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
news
How Can We Help You ?
We reaffirm the high quality service of "high quality, low cost", "integrity builds character, dedication to create quality" as the company's pursuit!
+86-0574-88473018 Contact UsWhat Is an Electrical Relay?
Posted by Admin | 25 Nov
Related Products
-
 Hehuaqiao,Yunlong,Yinzhou District,Ningbo,Zhejiang
Hehuaqiao,Yunlong,Yinzhou District,Ningbo,Zhejiang
-
 Tel:+86-0574-88473018
Tel:+86-0574-88473018
+ 86-0574-88344018 -
 Fax:+86-574-88345918
Fax:+86-574-88345918
-
 E-mail: sales@helishun.com
E-mail: sales@helishun.com
sales2@helishun.com
About us
Ningbo Helishun Electron Co.,Ltd. is founded in 2000, located at Ningbo City, the Grand East port on the coastline of the East Sea. We are OEM/ODM Electromagnetic Relays Manufacturers in China
Extra links
QR code
Copyright © Ningbo Helishun Electron Co.,Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Electrical Relays Suppliers


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体