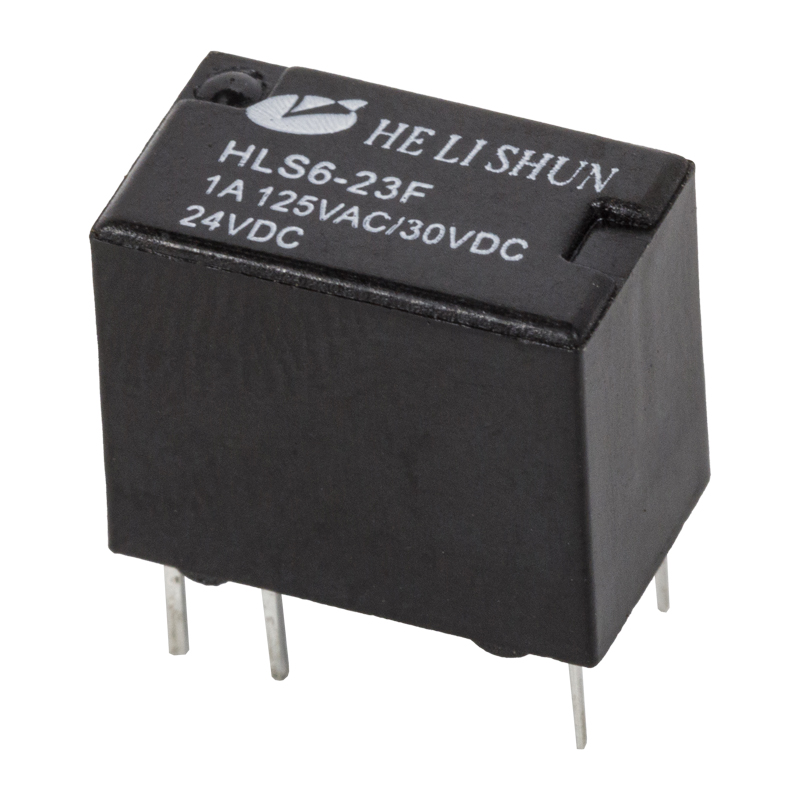
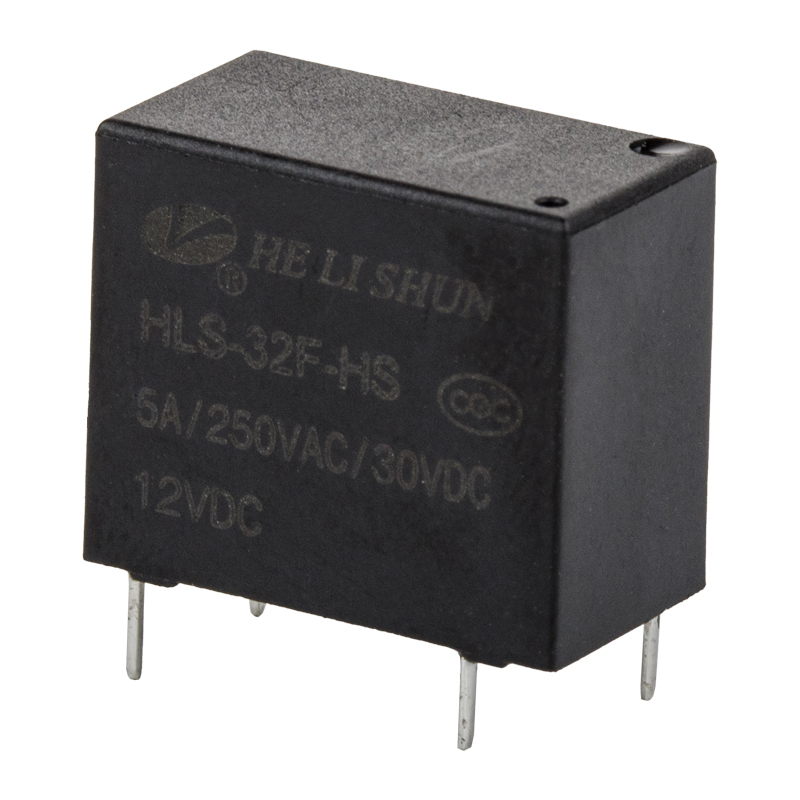
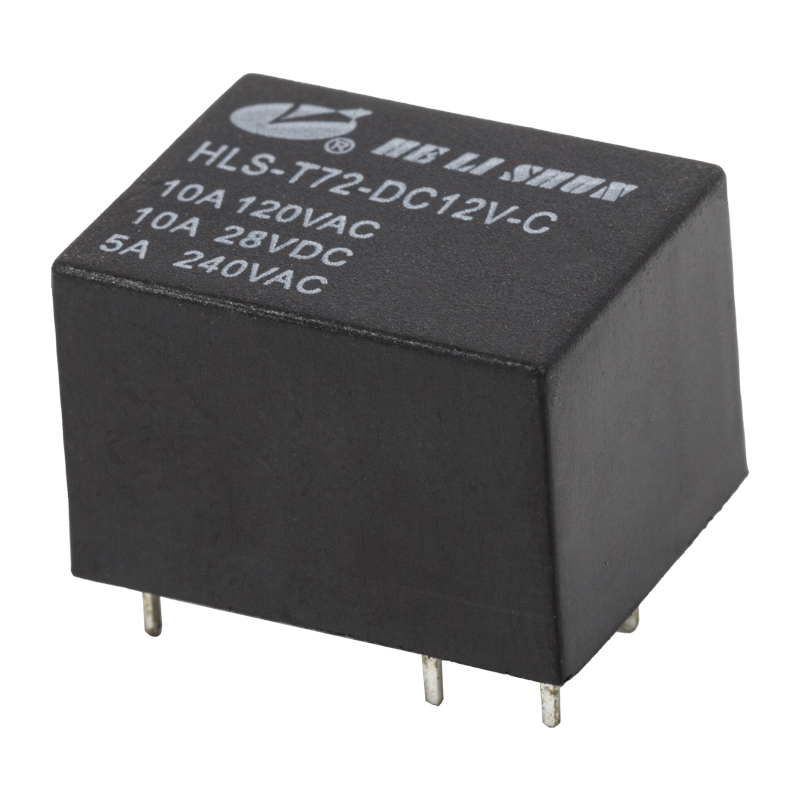
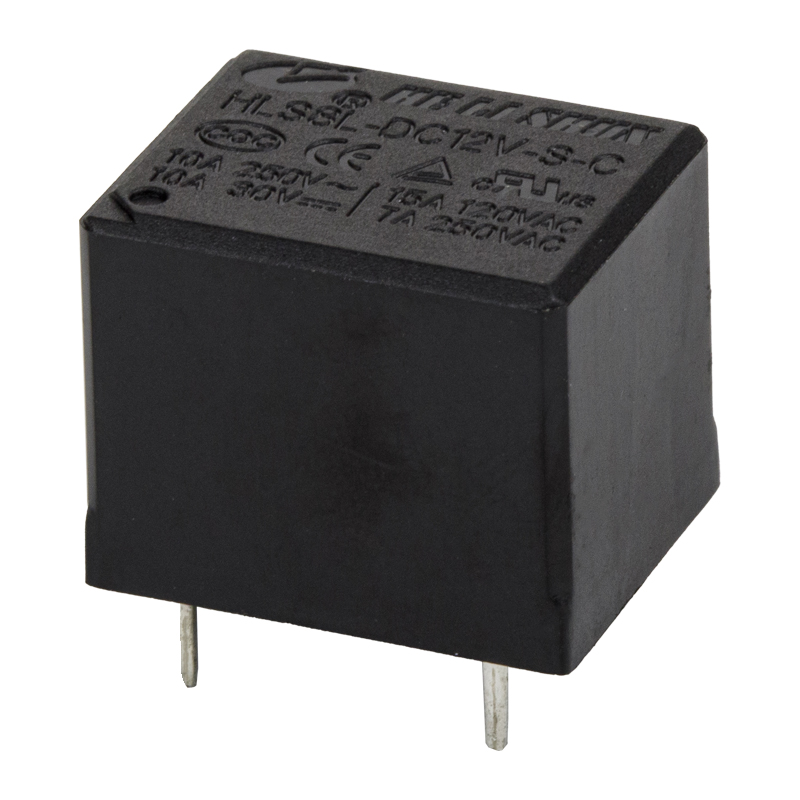
Relay generally refers to electromagnetic relay, that is, mechanical action. The essence of the relay's working principle is to use one circuit (generally small current) to control the on-off of the other circuit (generally large current), and during this control process, the two circuits are generally isolated.
The basic principle of the relay is to use the electromagnetic effect to control the mechanical contact to achieve the purpose of making and breaking. It energizes the coil with iron core - the coil current generates a magnetic field - the magnetic field absorbs the armature to act on and off the contact. The whole process is a process of "small current - magnetic - mechanical - large current".
What is the use of relay
Relay is an automatic switching element with isolation function. When the change of excitation quantity in the input circuit reaches the specified value, it is an automatic circuit control device that can make the controlled quantity in the output circuit change in a predetermined step.
The relay has an induction mechanism that can reflect some external excitation (electric or non electric), an actuator that can control the controlled circuit "on" and "off", and an intermediate comparison mechanism that can compare, judge and convert the magnitude of the excitation.
Relays are widely used in remote control, telemetry, communication, automatic control, mechatronics, aerospace technology and other fields to control, protect, regulate and transmit information.
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
news
How Can We Help You ?
We reaffirm the high quality service of "high quality, low cost", "integrity builds character, dedication to create quality" as the company's pursuit!
+86-0574-88473018 Contact UsHow does the relay work
Posted by Admin | 02 Dec
Related Products
-
 Hehuaqiao,Yunlong,Yinzhou District,Ningbo,Zhejiang
Hehuaqiao,Yunlong,Yinzhou District,Ningbo,Zhejiang
-
 Tel:+86-0574-88473018
Tel:+86-0574-88473018
+ 86-0574-88344018 -
 Fax:+86-574-88345918
Fax:+86-574-88345918
-
 E-mail: sales@helishun.com
E-mail: sales@helishun.com
sales2@helishun.com
About us
Ningbo Helishun Electron Co.,Ltd. is founded in 2000, located at Ningbo City, the Grand East port on the coastline of the East Sea. We are OEM/ODM Electromagnetic Relays Manufacturers in China
Extra links
QR code
Copyright ? Ningbo Helishun Electron Co.,Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Electrical Relays Suppliers


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体