The four functions of DPDT relay manufacturer the relay are as follows:
First, expand the scope of control.
When the control signal of the multi-contact point miniature power relay reaches a certain value, it can be disconnected, switched, and connected to the multi-channel circuit at the same time according to the difference of the contact point group.
Two, get bigger.
Smart relays, positive intermediate relays, etc., can control very high-power circuits with a very small amount of control.
Third, comprehensive signals.
When several control signals are typed into the multi-winding small signal relay in the specified way, the predetermined control actual effect can be achieved by being more comprehensive.
Fourth, automatic, remote control, detection.
The relays in the protection device, together with other household appliances, can form a program flow control route to realize the operation of automation technology.
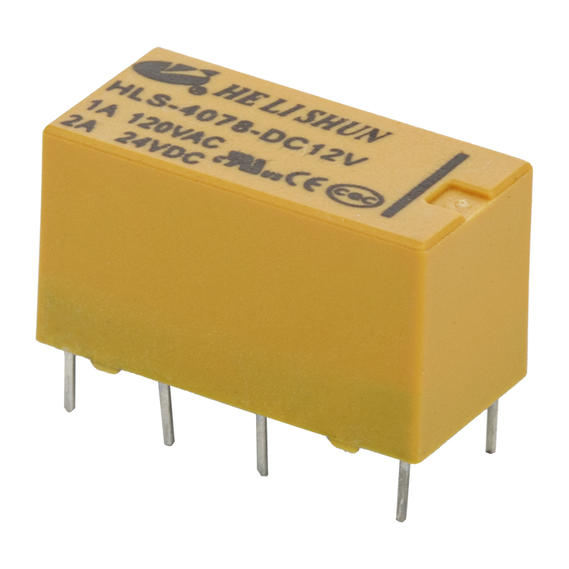
What is a relay? What does a small power relay do?
A relay is an electrical control device. It has an interactive relationship between the control system (also known as the input loop) and the controlled system (also known as the output loop). Usually used in automated control circuits, it is actually an "automatic switch" that uses a small current to control the operation of a large current. Therefore, it plays the role of automatic adjustment, safety protection, and conversion circuit in the circuit.
Its working principle is to use the interaction between the control system of the intermediate power relay and the controlled system. When the input quantity reaches the specified value, the relay makes the controlled output circuit turn on or off, so as to achieve the control effect. The input quantities here can be divided into two categories: electrical quantities (such as current, voltage, frequency, power, etc.) and non-electrical quantities (such as temperature, pressure, speed, etc.).
According to the principle of action, relays can be divided into:
1. Solid state relay:
A relay whose input and output functions are completed by electronic components without mechanical moving parts.
2. Electromagnetic relay:
Under the action of the current in the input circuit, a relay that produces a predetermined response by the relative movement of the mechanical parts. It includes DC electromagnetic relays, AC electromagnetic relays, magnetic latching relays, polarized relays, reed relays, and energy-saving power relays.
3. Time relay: when the input signal is added or removed, the output part needs to delay or limit the time to close or disconnect the relay of its controlled circuit.
4. Acceleration relay: When the acceleration of the moving object reaches the specified value, the controlled circuit will be connected or disconnected.
5. Wind speed relay:
When the wind speed reaches a certain value, the controlled circuit will be turned on or off.
6. Temperature relay: a relay that acts when the outside temperature reaches a specified value.
7. Other types of relays: such as photorelays, acoustic relays, thermal relays, etc.
The relay has the advantages of fast action, stable operation, long service life and small size. Widely used in power protection, automation, motion, remote control, measurement and communication devices.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体