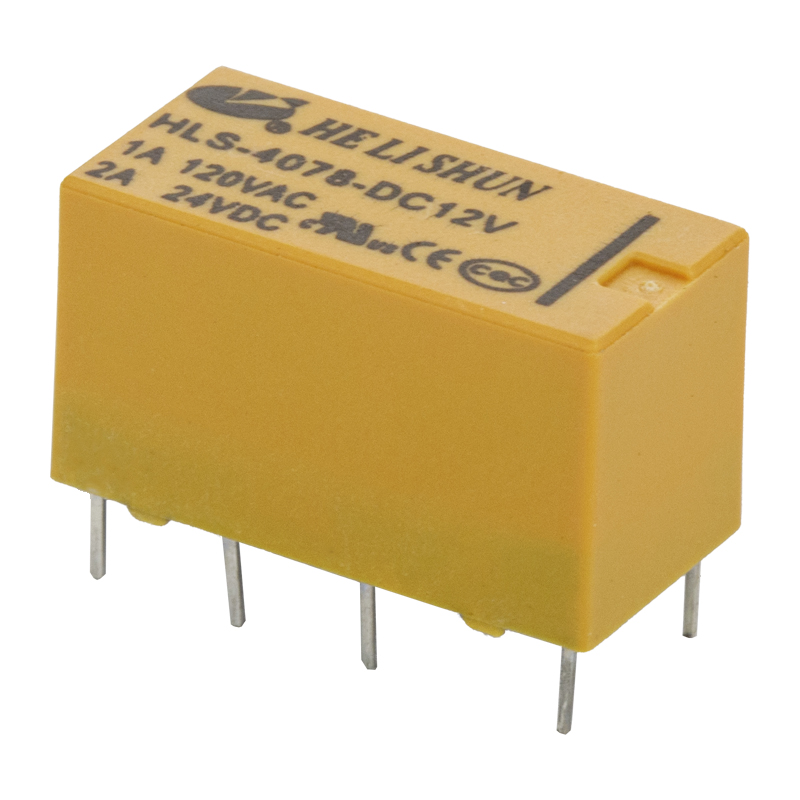
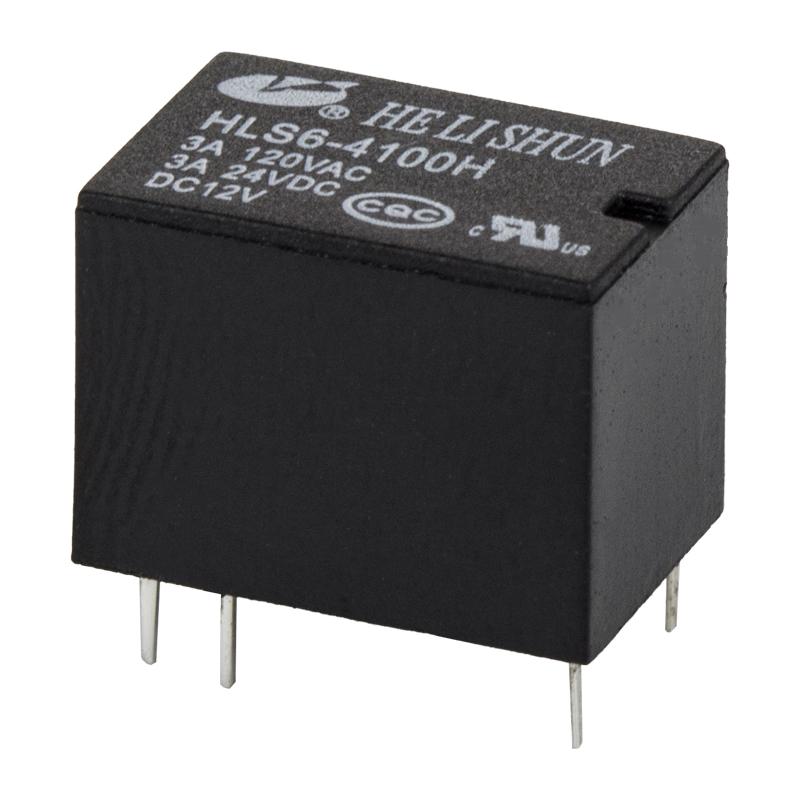
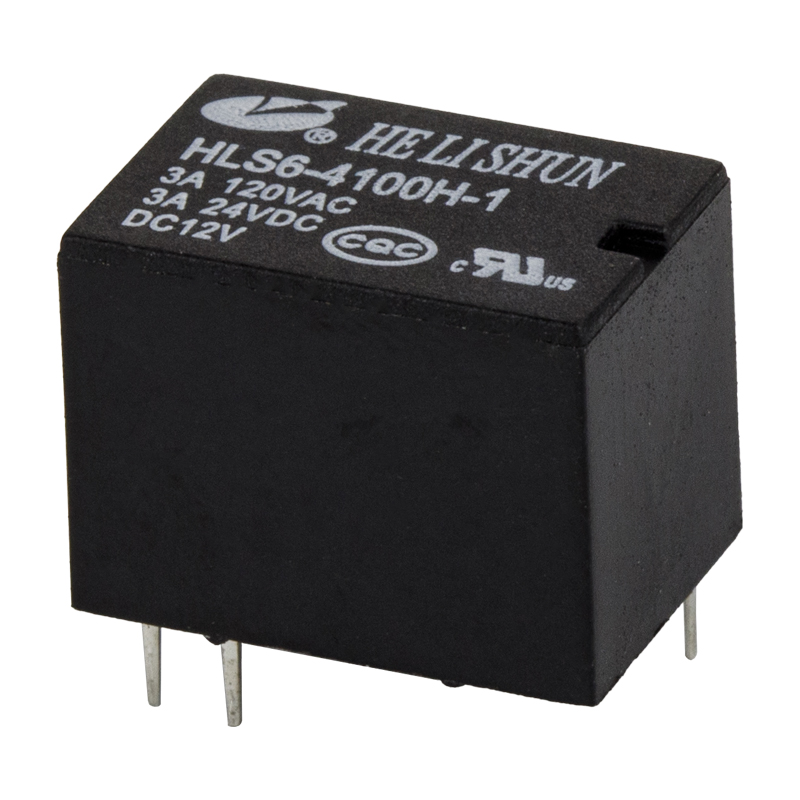
An electromagnetic relay is an electrical device used to make or break an electrical connection. It is a movable metal armature mechanically linked to one or more sets of contacts. This component is commonly used in the communication and automation field.Electromagnetic relays are similar to switches in that they use an electromagnet to trigger the switch. They are also similar to a split-phase induction motor, which works on a magnetic field.

There are four different types of electromagnetic relays. Each type has a different working mechanism. One of the most important parameters of an electromagnetic relay is its resistance. The coil resistance is closely related to the operating voltage. When an electromagnetic relay works properly, it will have a resistance between 10-500 Ohms.If you are installing an electromagnetic relay, you should perform an electromagnetic relay test to determine whether the coil is in an open or closed circuit. To do this, connect a multimeter to the coil terminals of the relay. Read the current and write down the voltage. Also, calculate the average value.
An electromagnetic relay is made up of an electromagnet, a coil, a movable iron armature, and springs. In simple relays, the coil is wrapped around a soft iron core. The armature is also wrapped in wire and held in place by a spring.In polarized type relays, the polarized coil acts as a magnet when the relay is energized. Similarly, in moving coil type relays, the coil is wound around a permanent magnet.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体