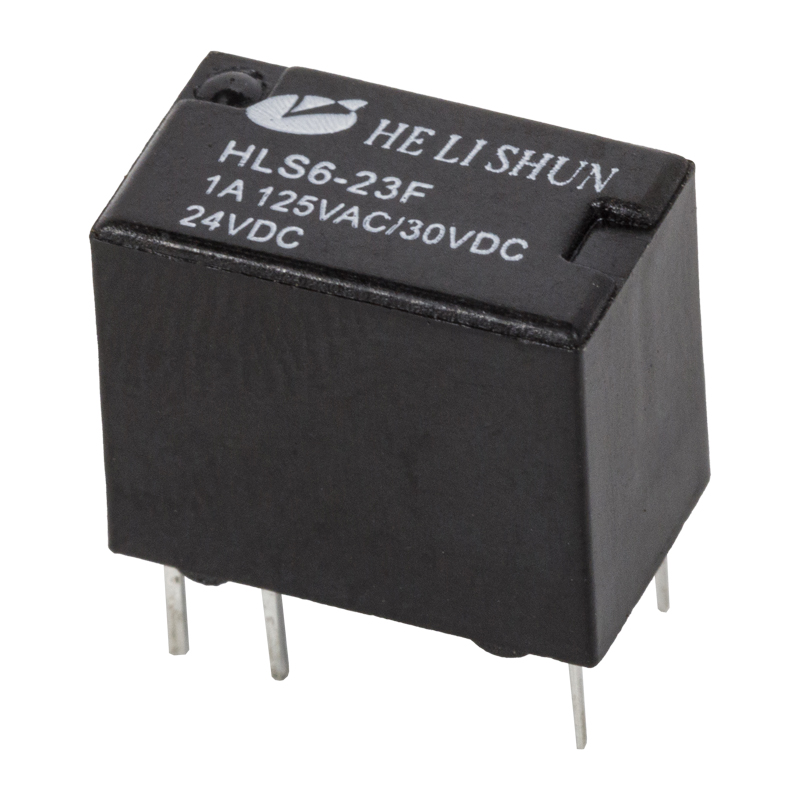
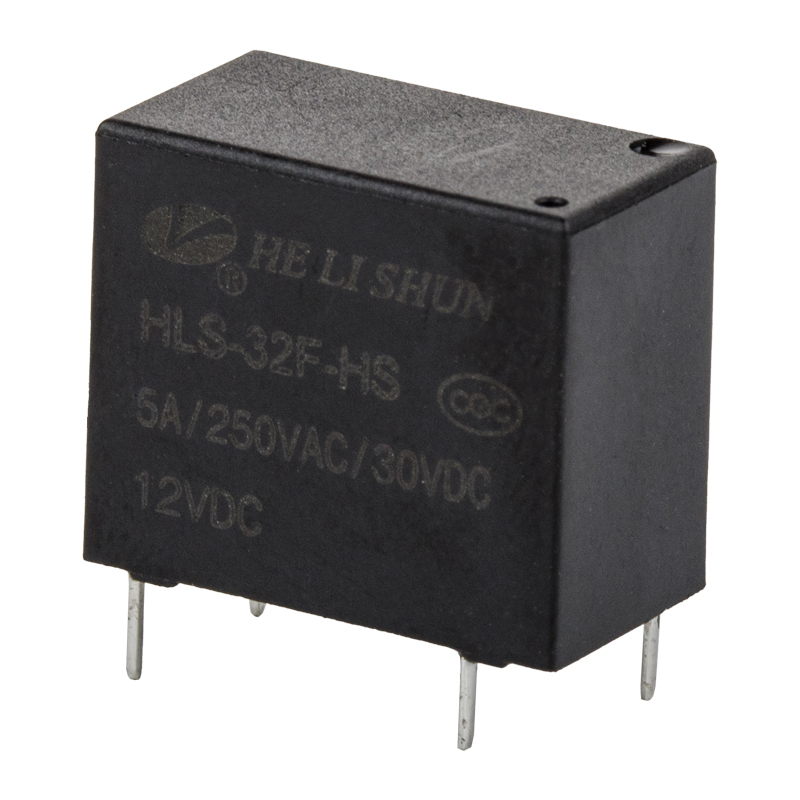
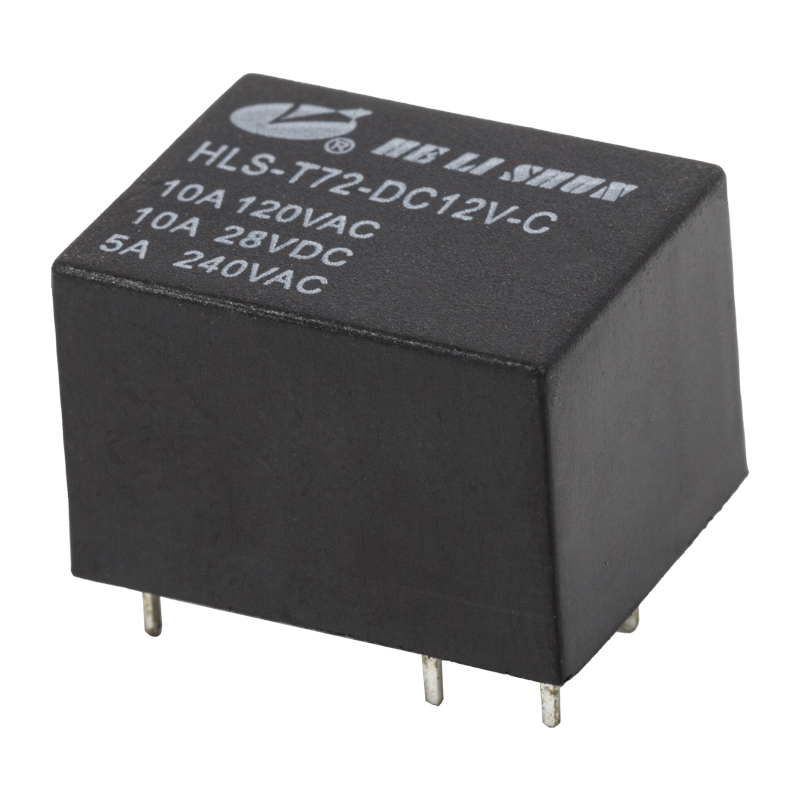
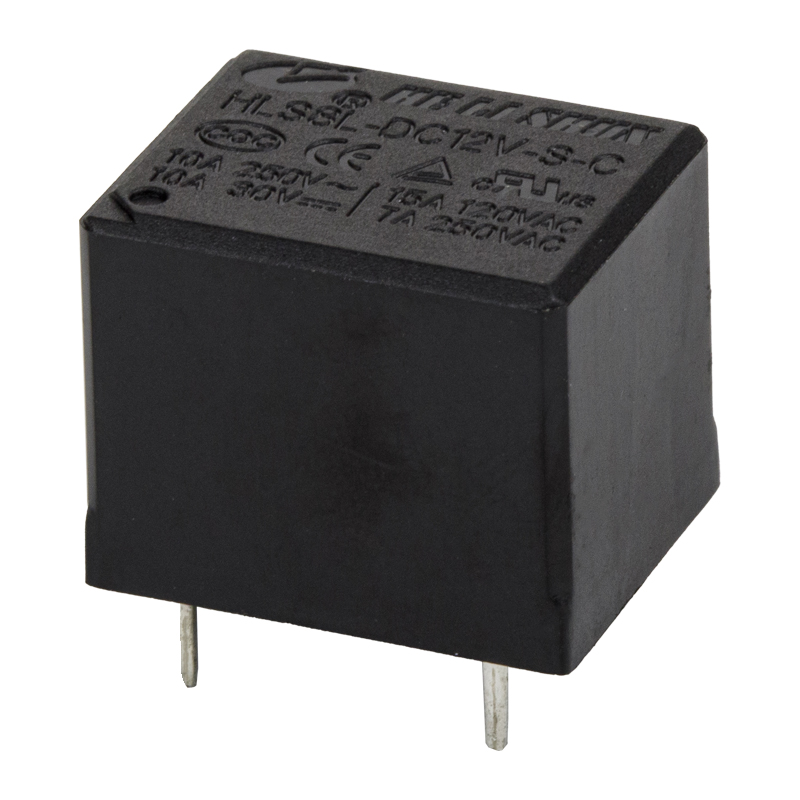
A power relay is a switch that uses an electromagnet to move an armature. The armature is the moving part of the switch and is surrounded by a frame. When the relay is powered, the coil draws the armature to the coil, where it is energized and pulled into contact. The armature is then returned to its original position by a spring.
The power relay is usually powered by a battery. The armature, a movable arm made of iron, attracts the electromagnet. It is held in place by a spring. The armature is then pulled in the direction of the coil, reaching a contact and closing the circuit. The opposite occurs when the armature is released.
One common problem with high-voltage power relays is arcing. Arcing occurs when the contacts of the relay are open at the same time, causing a high amount of heat in the device. This in turn decreases the lifespan of the relay. One common way to troubleshoot a power relay is to use a multimeter and use its continuity feature.
There are many uses for a power relay. They can be used to protect devices from noise and to give a signal when the voltage changes. A wide range of different relay types and styles is available.
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
news
How Can We Help You ?
We reaffirm the high quality service of "high quality, low cost", "integrity builds character, dedication to create quality" as the company's pursuit!
+86-0574-88473018 Contact UsWhat is a Power Relay?
Posted by Admin | 02 Sep
Related Products
-
 Hehuaqiao,Yunlong,Yinzhou District,Ningbo,Zhejiang
Hehuaqiao,Yunlong,Yinzhou District,Ningbo,Zhejiang
-
 Tel:+86-0574-88473018
Tel:+86-0574-88473018
+ 86-0574-88344018 -
 Fax:+86-574-88345918
Fax:+86-574-88345918
-
 E-mail: sales@helishun.com
E-mail: sales@helishun.com
sales2@helishun.com
About us
Ningbo Helishun Electron Co.,Ltd. is founded in 2000, located at Ningbo City, the Grand East port on the coastline of the East Sea. We are OEM/ODM Electromagnetic Relays Manufacturers in China
Extra links
QR code
Copyright ? Ningbo Helishun Electron Co.,Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Electrical Relays Suppliers


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体