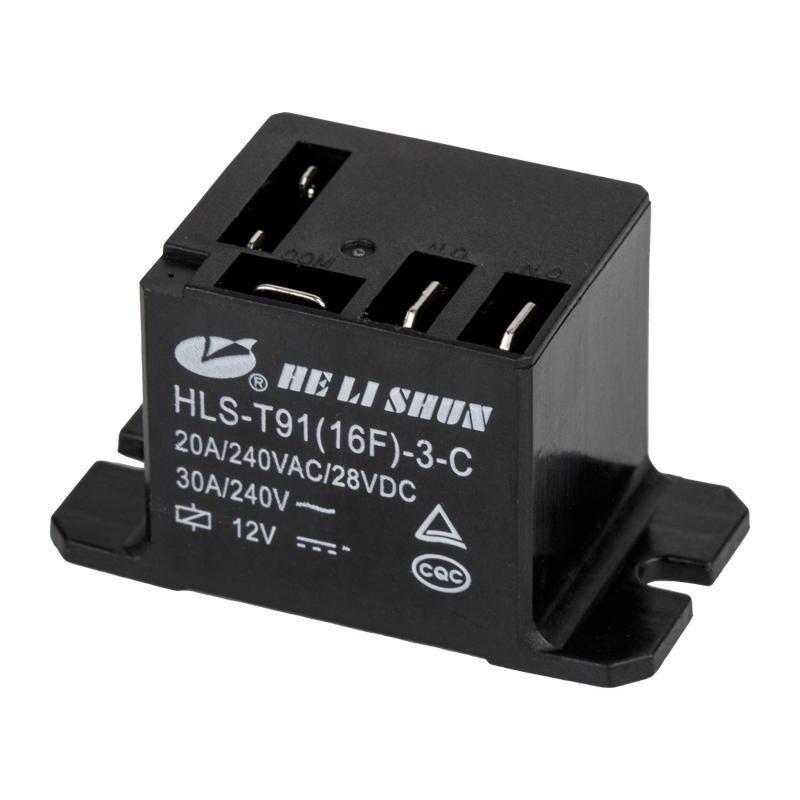
Choosing the right PCB (Printed Circuit Board) power relay is important to ensure reliable and efficient control of power circuits. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a PCB power relay:
Current Rating: Determine the current rating required for your application. This is the maximum amount of current that the relay can handle without exceeding its specifications. Ensure that the relay's current rating is suitable for the load you intend to control. It is advisable to choose a relay with a slightly higher current rating than the expected load to provide a safety margin.
Voltage Rating: Consider the voltage rating of the power relay. It should match or exceed the voltage of the circuit it will be used in. Ensure that the relay can handle the maximum voltage of your application without compromising safety or performance.
Contact Configuration: Determine the appropriate contact configuration for your application. PCB power relays come in various configurations, such as normally open (NO), normally closed (NC), or changeover (CO). Select the contact configuration that suits your circuit requirements and the desired switching behavior.
Coil Voltage: Choose a power relay with a coil voltage that matches the control voltage of your circuit. The coil voltage determines the voltage required to energize the relay and activate its contacts. Ensure that the coil voltage matches the voltage available in your circuit to ensure proper operation.
Switching Speed: Consider the switching speed required for your application. Power relays have different response times or switching speeds. Some applications may require fast switching, while others may tolerate slower response times. Determine the appropriate switching speed based on your circuit requirements.
Size and Mounting: Consider the physical size and mounting options of the PCB power relay. Ensure that the relay's dimensions and pin configuration are compatible with your PCB layout and available space. Choose a relay that can be easily mounted on your PCB using suitable soldering or mounting techniques.
Reliability and Durability: Evaluate the reliability and durability of the power relay. Look for relays from reputable manufacturers known for producing high-quality components. Consider factors such as the relay's lifespan, electrical endurance, and resistance to environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and vibration.
Additional Features: Determine if your application requires any additional features, such as built-in protection circuits (e.g., diodes or snubbers) or specialized functionality (e.g., latching or time-delayed relays). Select a power relay that offers the desired features to meet your specific application requirements.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体