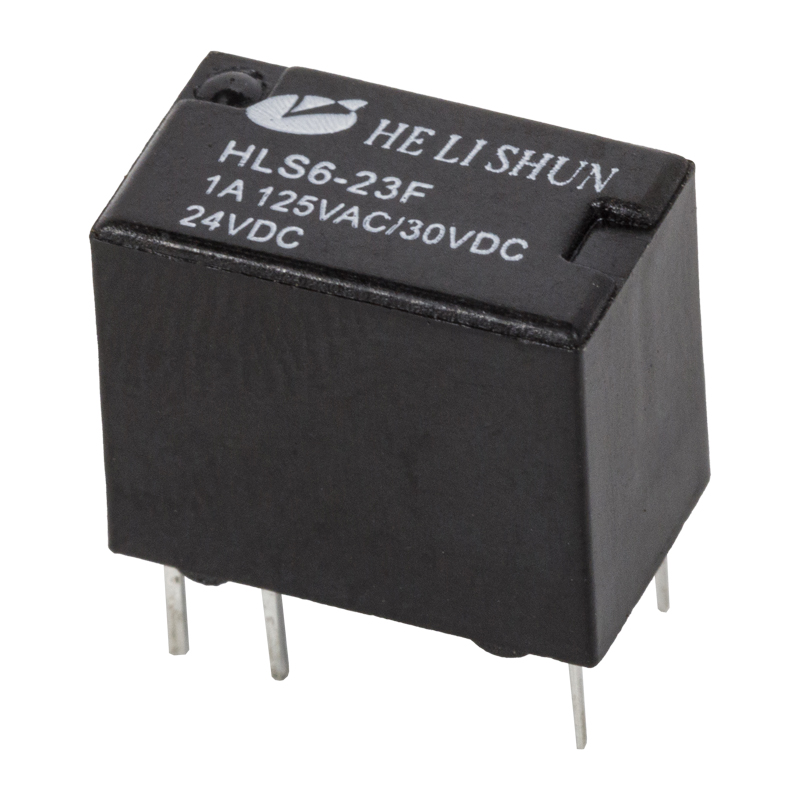
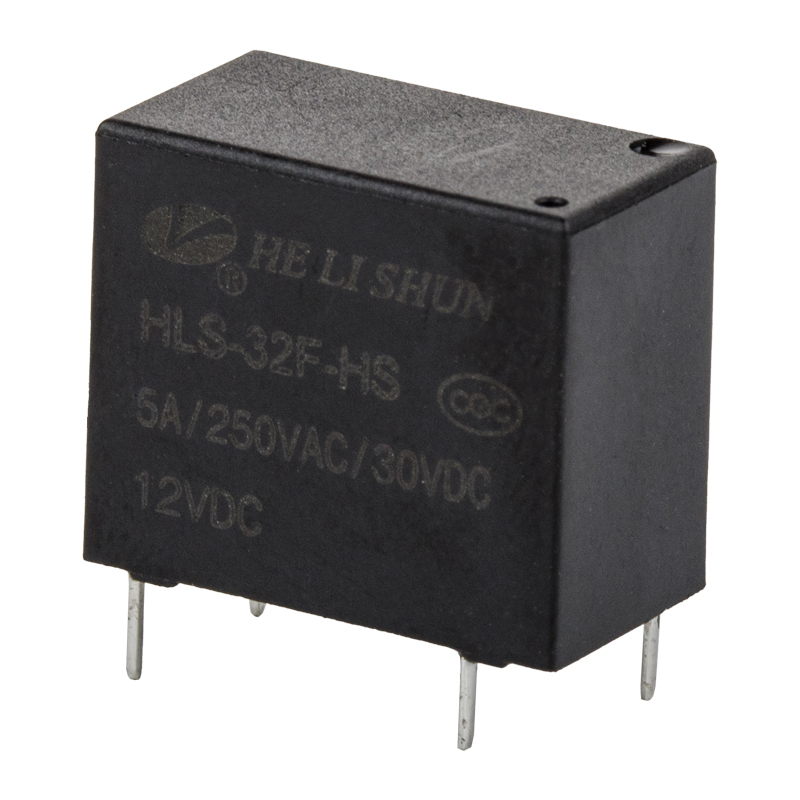
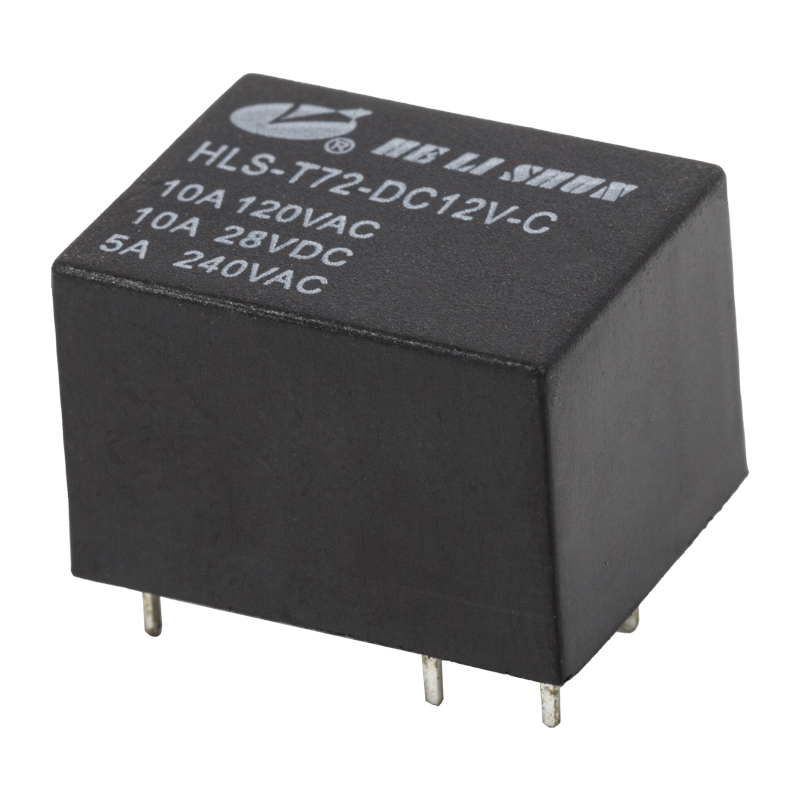
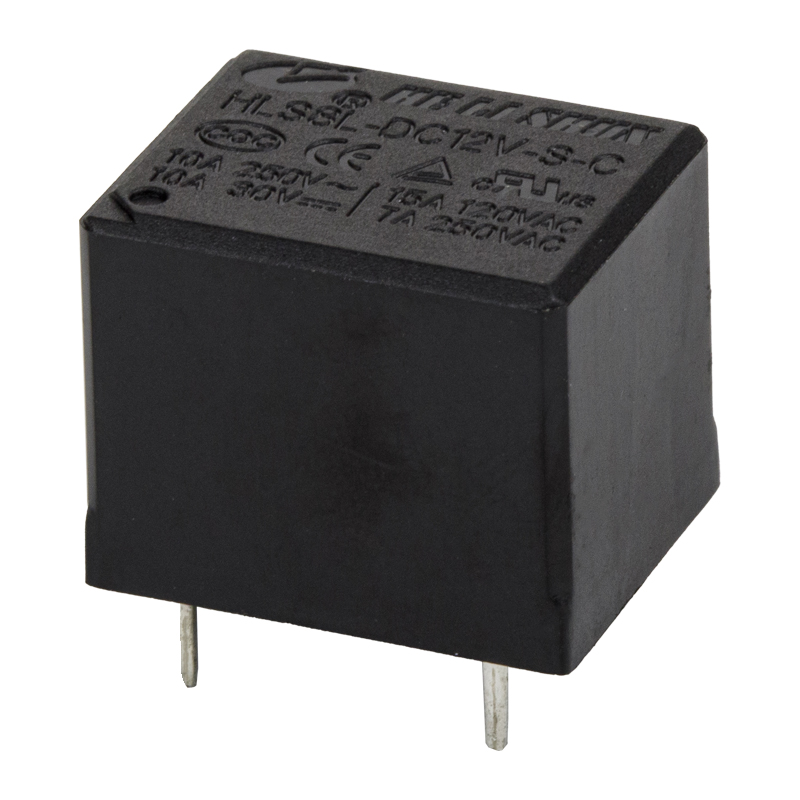
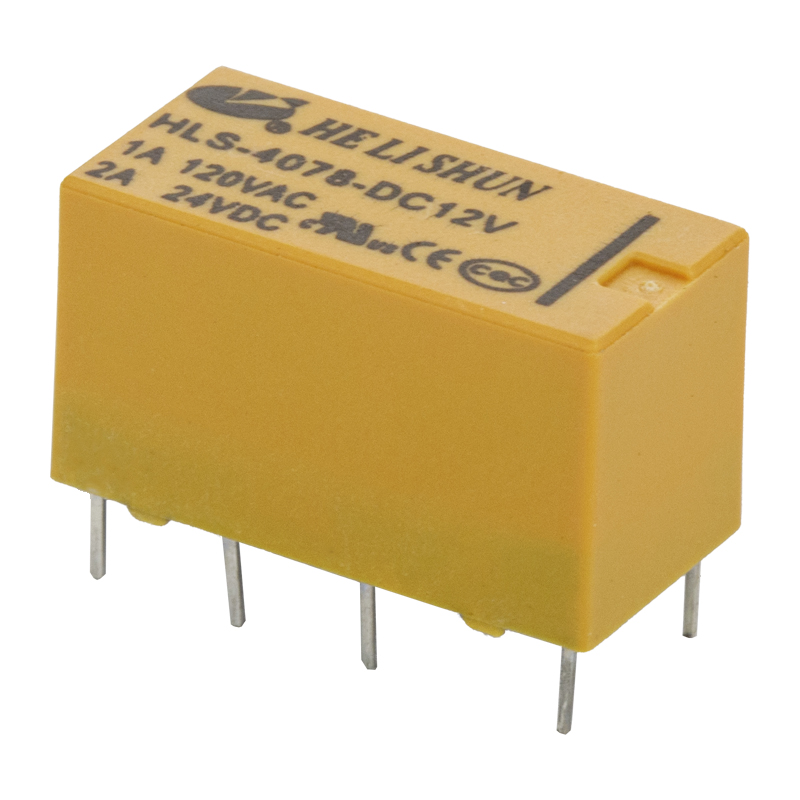
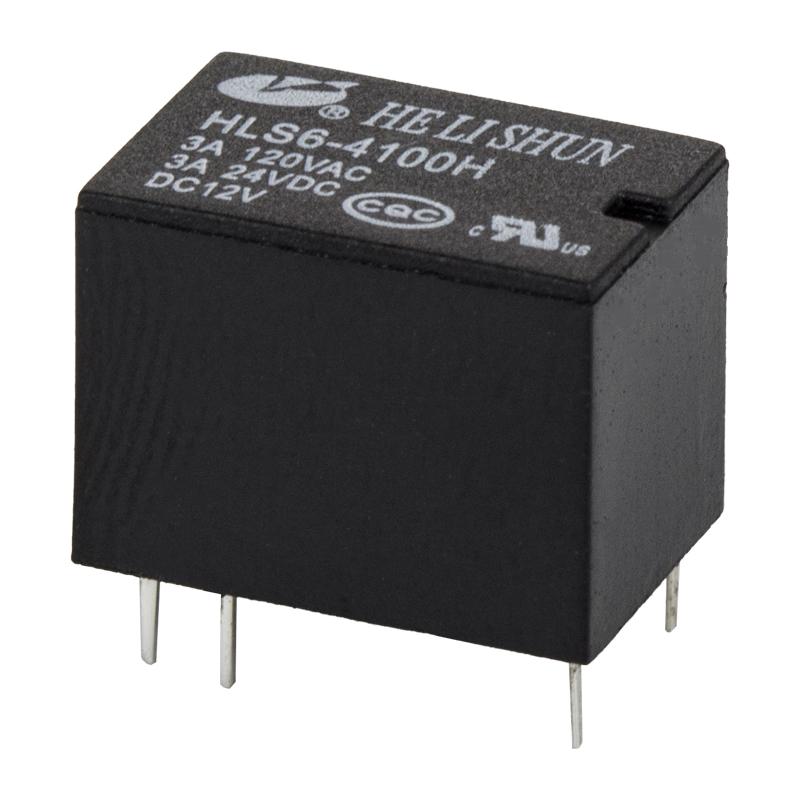
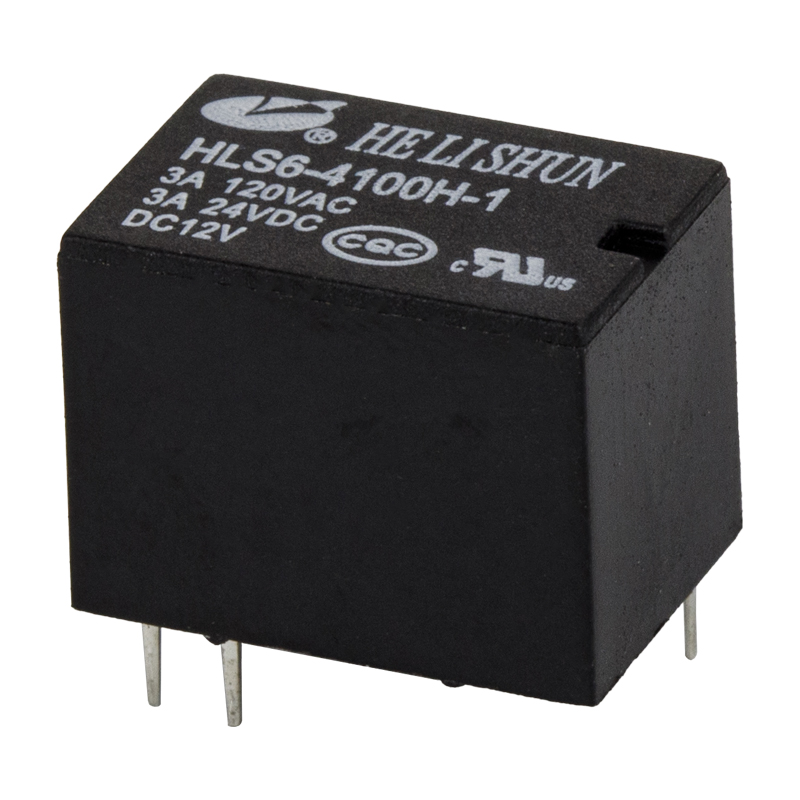
The development of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) power relay has been a major breakthrough in the field of electronic components. A PCB power relay is an electro-mechanical switch that is used to control the flow of current in a circuit. It is mounted on a printed circuit board, which allows for easier installation and wiring.
Here are some of the key developments in the history of PCB power relay:
Miniaturization: Over time, PCB power relays have become smaller and more compact, allowing for greater flexibility in designing and assembling electronic devices. This has led to the development of miniature PCB power relays, which are commonly used in a variety of applications, including home appliances, automotive electronics, and industrial automation.
Improved Performance: Advances in materials and design have led to improvements in the performance of PCB power relays, including higher switching speeds, lower contact resistance, and increased reliability. This has made them more suitable for use in high-speed and high-power applications.
Diversification: PCB power relays have become more diverse in terms of their capabilities and functions. For example, some relays are designed for high-voltage or high-current applications, while others are optimized for low-power or low-voltage applications. Additionally, some PCB power relays are equipped with advanced features such as sealed enclosures, latching mechanisms, and surge protection.
Integration with other Components: PCB power relays are often integrated with other electronic components, such as transistors, diodes, and resistors, to create more complex circuits. This has led to the development of integrated circuits (ICs) and system-on-chip (SoC) solutions, which combine multiple functions into a single package.
Overall, the development of PCB power relays has played a critical role in the advancement of electronic devices and systems. Their compact size, improved performance, diversification, and integration with other components have made them an essential component in many modern electronic devices.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体